牛顿方法的关键是找到一个较好的初值。
同伦算法(Homotopy method, continuation method, successive loading method)可以用来生成一个较好的初值。
是一个已知函数,它的零点已知,
构造一个一个依赖于参数的函数
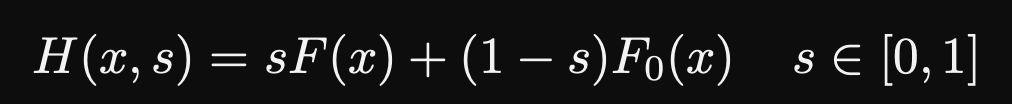 的解为 的解, 的解为 的解。
的解为 的解, 的解为 的解。
的一种构造方式为
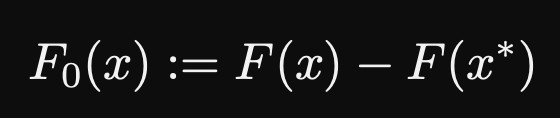 同伦方程(Homotopy function)为
同伦方程(Homotopy function)为
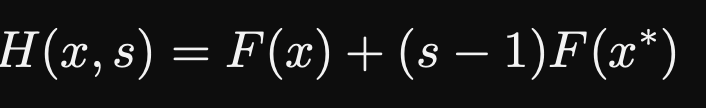
的解与 有关,将它记为 ,当 趋于 , 趋于 。
选取一些列
通过牛顿方法求解一系列非线形问题
每个问题都用 作为迭代初值。
例子
对于问题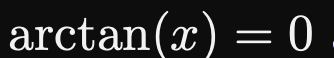 ,如果用牛顿迭代方法求解,当
,如果用牛顿迭代方法求解,当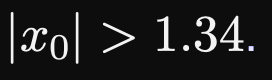 时不收敛,如果用同伦算法求解,即使迭代初值为4,也能收敛。
时不收敛,如果用同伦算法求解,即使迭代初值为4,也能收敛。
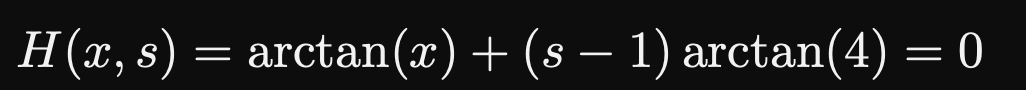
代码
def newton_iteration(f, df, x0, tol=1e-3, max_iter=100):
"""
牛顿迭代算法
参数:
f: 待求根的函数
df: f的导数函数
x0: 初始猜测值
tol: 迭代终止容差,默认为1e-6
max_iter: 最大迭代次数,默认为100
返回:
root: 方程的近似根
iterations: 迭代次数
"""
x = x0
for i in range(max_iter):
# 计算牛顿迭代步骤
x_new = x - f(x) / df(x)
# 检查是否收敛
if abs(x_new - x) < tol:
return x_new, i + 1
x = x_new
print(x)
raise ValueError("未能在给定迭代次数内收敛到解")
import numpy as np
# 示例:求解方程x^3 - 2x - 5 = 0的根
# 定义函数及其导数
def f(x):
return np.arctan(x)
def df(x):
return 1.0/(1.0+x*x)
# 初始猜测值
x0 = 1.3
# 调用牛顿迭代算法求解
root, iterations = newton_iteration(f, df, x0)
print("方程的根: ", root)
print("迭代次数: ", iterations)
# 同伦方程
def hf(x,s):
return np.arctan(x)+(s-1)*np.arctan(x0)
def hdf(x,s):
return 1.0/(1.0+x*x)
x0=4
n = 10
result = []
s=np.linspace(1e-5,1,n)
# 同伦算法
for i in s:
def f(x):
return hf(x,i)
def df(x):
return hdf(x,i)
root, iterations = newton_iteration(f, df, x0)
print("方程的根: ", root, "s=",i)
print("迭代次数: ", iterations)
x0=root
result.append(root)
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.plot(s,result)
plt.show()